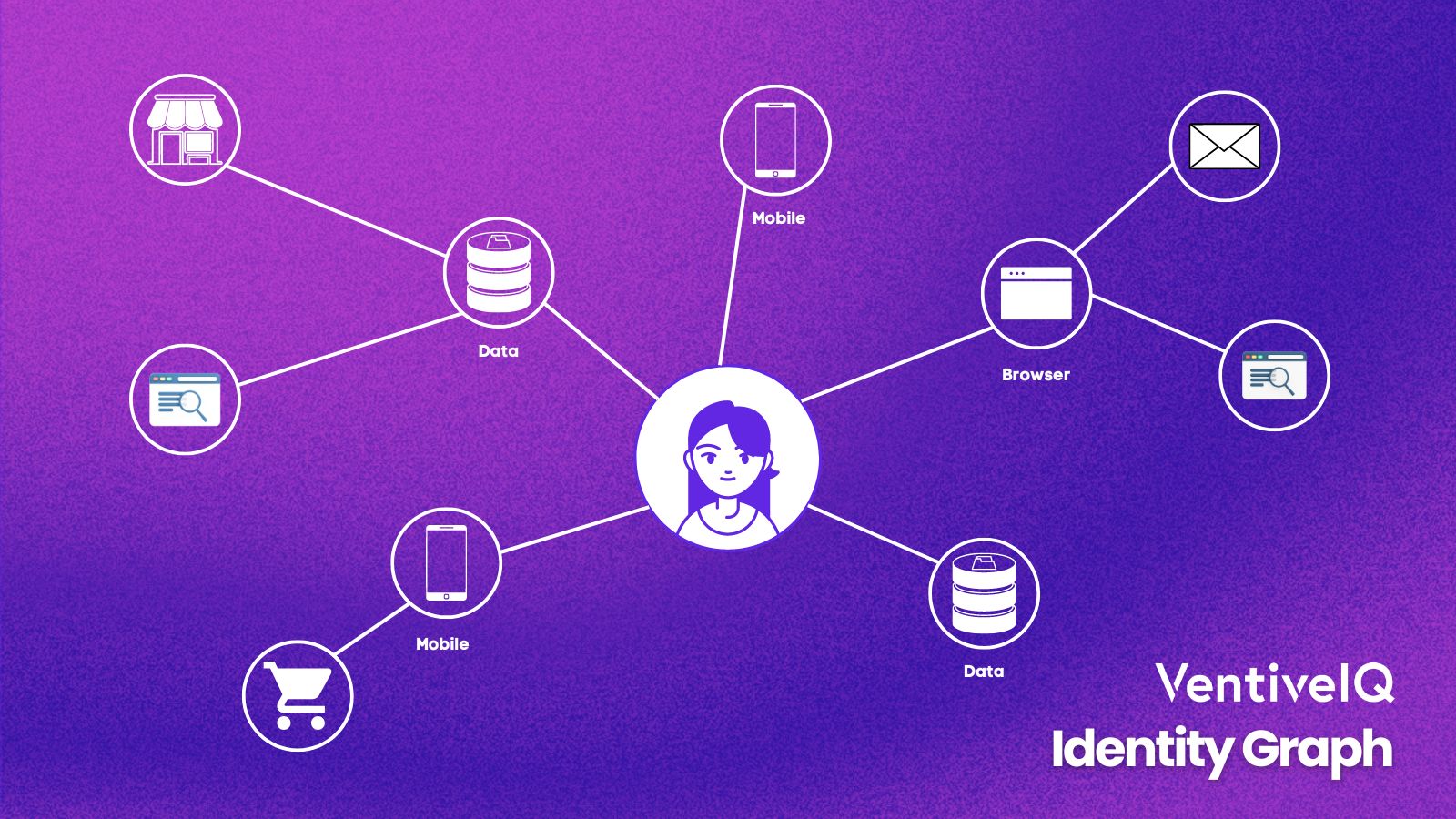
An identity graph, also known as a customer identity graph, is a collection of data that is used to identify and link individuals across various digital devices, channels and platforms. It is a database that maps user behavior and interactions across different touchpoints, such as websites, desktops, mobile apps, tablets, social media and email, to a single user profile.
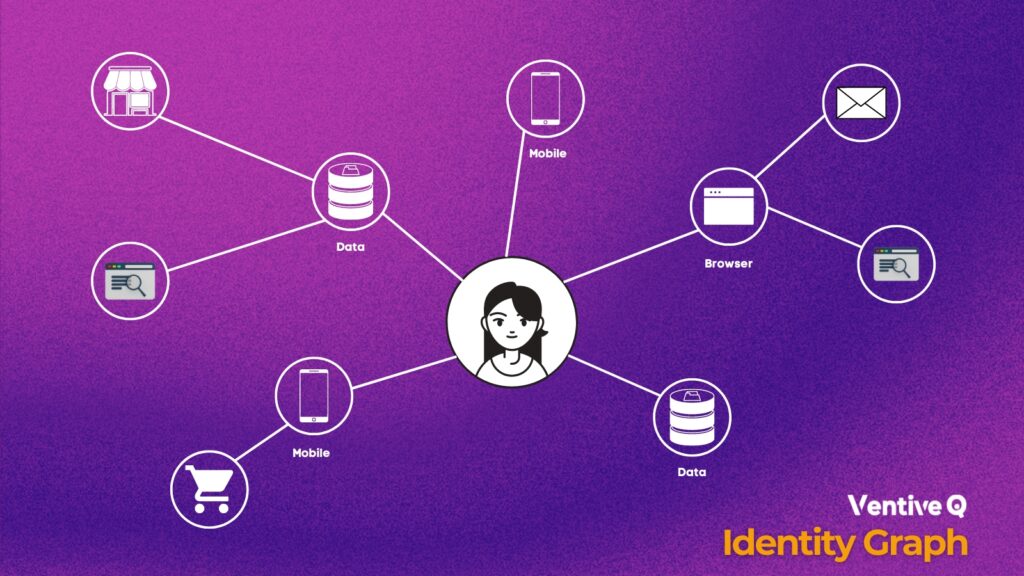
An identity graph typically includes data such as First Name, Last Name, physical address, Demographic, Mobile Ad IDs, Device IDs, IP addresses, User Agent Strings, Cookie, email addresses, social media profiles, and other identifiers that can be used to track a user’s activity. This data is collected and organized using various technologies, such as cookies, browser fingerprinting, and device graphing.
Many companies do not keep privacy-safe first-party data stores and prefer to focus on the execution of their marketing campaigns using VentiveIQ privacy-safe data to put VentiveIQ data to work for you. Learn how to take control of your company’s data-driven future.
The objective of an identity graph is to provide a comprehensive view of each individual’s identity, interests, behaviors, and preferences, which can help businesses better understand their selective and create more personalized and effective marketing campaigns. An identity graph is built using data from various sources, including cookies, logins, social media profiles, and customer databases – it uses algorithms to match and link data points to make a unified customer profile.
Generally, an identity graph enables businesses to track and understand the behavior of their customers across multiple touchpoints, allowing them to provide more personalized and compelling experiences, such as personalized content, recommendations, and offers. The data gathered through an identity graph can also help businesses optimize their marketing campaigns by identifying which channels and tactics are most effective for reaching and engaging their selective.
The use of identity graphs has become increasingly important as customers engage with businesses through multiple channels and devices, and as the amount of data generated grows. By using an identity graph, businesses can better understand their customers and provide more relevant and personalized experiences, leading to increased customer loyalty and revenue.
Probabilistic Matching and Deterministic Matching
Two types of matching algorithms are employed to stitch the profiles, namely deterministic and probabilistic.
Deterministic Matching
-
- Deterministic matching is a strategy used to match two or more data records with a high level of confidence, by using a unique identifier that is present in all the records. The process involves comparing the available data fields in the records and identifying the area that contains a unique identifier, such as a hashed email address, phone number, or social security number. Deterministic matching is considered to be highly accurate because the unique identifier is usually associated with a single individual, making it likely to link data across multiple sources with precision.
- Deterministic matching is generally used in various fields such as marketing, customer relationship management (CRM), fraud detection, and identity verification. It is likewise used in healthcare to match patient records across different systems, ensuring that the right medical data is associated with the correct patient.
Probabilistic Matching
-
- Probabilistic matching is a method of stitching data from multiple sources, such as databases or social media profiles, where there is no unique identifier to link the data together. Probabilistic matching utilizes a set of characteristics or identifiers, such as IP address, device type, browser, operating system, location, and other data points, to evaluate the probability of two or more records belonging to the same individual or entity.
- The process involves comparing the available data points across multiple records and computing a probability score that describes the possibility of a match. The higher the score, the greater the probability that the records belong to the same person. However, unlike deterministic matching, probabilistic matching is not always 100% accurate and may sometimes result in false matches or misses.
Applications of Identity Graph
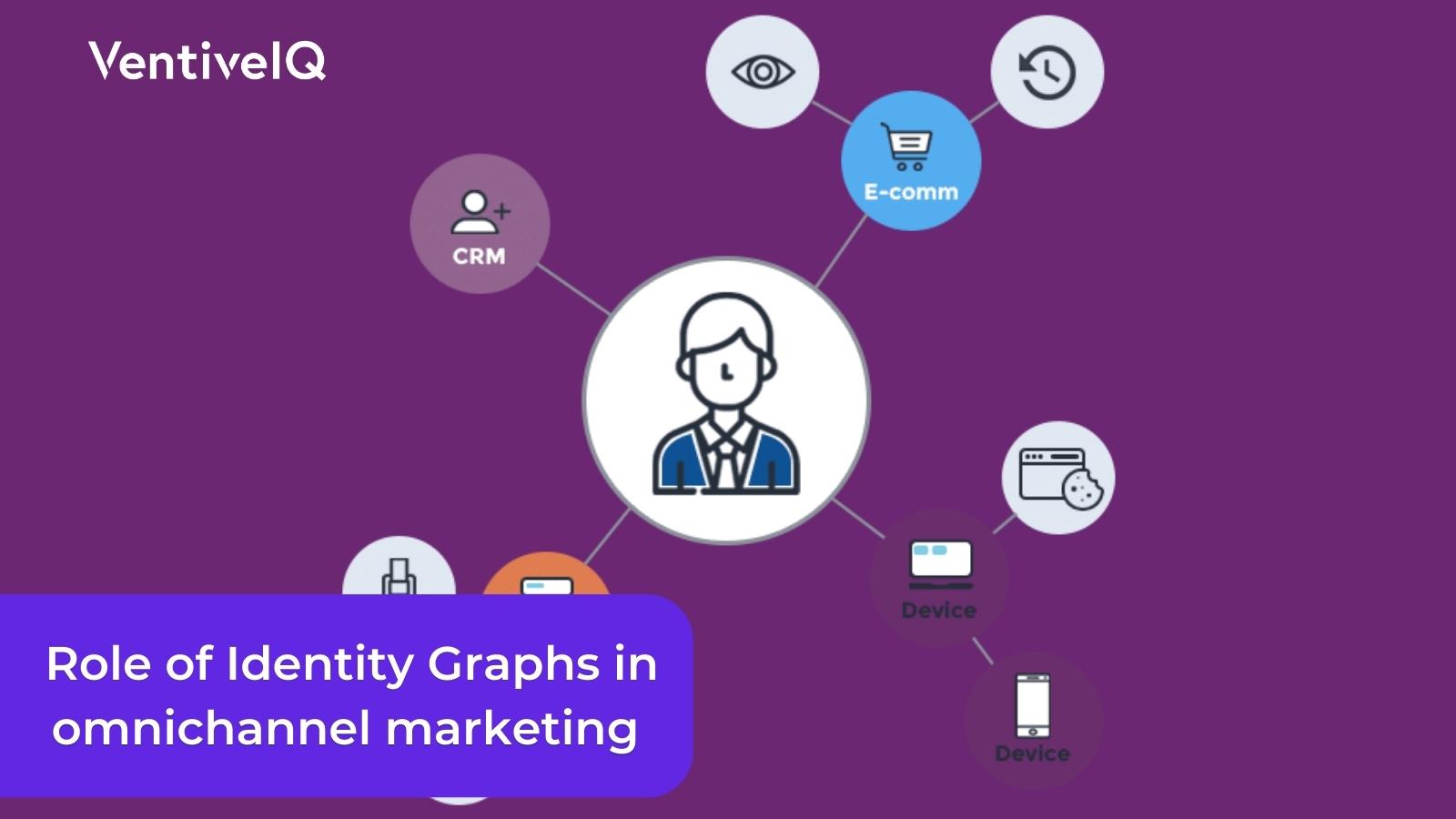
The primary role of identity graphs is to connect customer identities and create a comprehensive and up-to-date view of their attributes and behaviors, known as a “single view of the customer.” This allows businesses to utilize the identity graph for several purposes, comprising of:
-
- Personalized customer service: Customer service agents typically use multiple tools to help customers. An identity graph consolidates data from various sources, providing agents with a complete understanding of the customer’s context. This allows them to quickly and efficiently address customer queries.
- Cross-device attribution: Customers interact with businesses through multiple channels. Identity graphs help businesses determine the role of the individual channel in converting clients. This enables businesses to make informed decisions when allocating marketing budgets.
-
- Personalized in-app experiences: Companies like Netflix and Amazon use identity graphs to track user browsing history across devices and screens. This enables them to recommend the most relevant content based on the user’s screen and time. For instance, a video website may customize its home page with short videos for users accessing content on mobile during their commute.
- Effective promotions: Identity graphs enable businesses to track how customers interact with promotions and deliver context-aware messaging on the appropriate screen at the right time. Workflows can be set up to deliver multi-stage messaging, where users receive different messages depending on their stage in the conversion cycle.
-
By linking different pieces of data related to a user’s identity, such as their email address, social media profiles, and browsing behavior, an identity graph can provide a comprehensive view of a customer’s interests, preferences, and behaviors.
Know more elements to consider while creating an identity graph.
Conclusion
With this information, businesses can tailor their messaging and content to better resonate with individual users, leading to improved engagement and conversion rates. However, it is essential to ensure that the collection and use of data within an identity graph are done transparently and ethically, with proper consent and protection for user privacy.
Overall, the use of identity graphs is likely to grow as businesses seek to provide more personalized experiences to their customers but, it will be significant to balance the benefits with the responsibility to protect user privacy and data security.